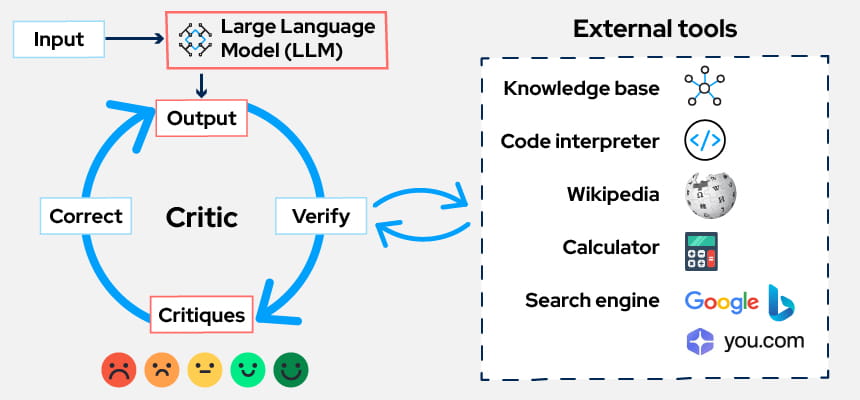
You can think of it as the AI doing an internal “quality check” on its own output, either by using external tools, external validators or its own reasoning loop with LLM as a critique. The AI effectively asks itself questions like:
- Did my answer follow the instructions correctly?
- Are there any gaps or contradictions?
- Can I make this clearer, safer, more accurate, or more aligned with the goal?
This reflective behavior helps reduce hallucinations, enhances reasoning depth, and leads to more reliable outcomes, especially in complex enterprise workflows where accuracy, safety, and consistency matter more than speed.
Reflection usually happens in three stages:
- Generate: the AI produces an initial answer.
- Reflect: the AI critiques its own answer, identifies issues, or proposes improvements.
- Refine: it rewrites or optimizes the response based on the reflection.
This internal loop can run once or iteratively to improve the output step-by-step.
Reflection Agent for Incident Root Cause Analysis in a Large Tech Company
Imagine a large enterprise, say a global financial services company that uses an AI agent internally to help engineers investigate production incidents.
When a critical outage occurs, the AI agent is given logs, error traces, and alerts. It needs to identify the most likely root cause and propose next steps.
Why This Pattern Matters in the Enterprise
Large organizations rely on accuracy and risk-free decisions. AI that can reflect before acting becomes:
- More reliable (reduces false positives and hallucinations)
- More trustworthy (the reasoning is tighter and internally validated)
- More efficient (engineers spend less time cleaning up bad AI recommendations)
- More aligned with enterprise governance (reflection catches policy or safety violations before output)
When applied to areas like incident response, financial analysis, compliance workflows, or medical triage, the reflection pattern drastically improves the quality and safety of AI actions.
One of the Use Cases of Reflection Pattern is Self-RAG (Proposed in SELF-RAG: LEARNING TO RETRIEVE, GENERATE, AND CRITIQUE THROUGH SELF-REFLECTION Paper)
Self-RAG is, at its core, a very practical example of the Reflection Pattern in action. Reflection is all about giving the model a moment to pause, look back at what it just produced, and ask itself, “Does this actually make sense?”
Self-RAG does the exact same thing, just in a more structured way.
To understand the benefit of this, it helps to briefly revisit how traditional RAG works. In a standard Retrieval-Augmented Generation pipeline, the system retrieves a fixed set of documents based on the user's query and then generates an answer conditioned on that retrieved context. While this improves factual grounding compared to a standalone LLM, the process is largely single pass: retrieval happens once, generation happens once, and the model does not explicitly verify whether the retrieved evidence was sufficient, relevant, or correctly used. As a result, errors such as incomplete answers, over-reliance on weak sources, or hallucinations can still slip through when retrieval quality or context alignment is suboptimal.
In the Reflection Pattern, the model reviews its own output and tries to spot gaps, mistakes, or contradictions. In Self-RAG, that reflective habit is applied specifically to retrieved information. Instead of assuming every retrieved document is useful or accurate, the model uses a small internal loop that mirrors the reflection idea:
- it generates a piece of text,
- steps back from it,
- critiques its own reasoning,
- labels parts as relevant, irrelevant, or only partially supported,
- and then rebuilds the final answer using only the pieces that passed its own review.
So, while retrieval gives the model the raw material, the reflection step is what keeps the final answer grounded and prevents it from drifting into guesses or blended facts.
In the example from the diagram, you can see this clearly. Self-RAG doesn’t just pull three passages and dump them into one answer. It produces small answers for each passage, critiques each one, and then depends on that internal reflection to choose the best-supported segments. Without that reflection loop, it would fall back to old RAG behavior mixing everything together, including the parts that didn’t actually line up with the retrieved text.
Self-RAG is reflection with a purpose. Instead of reflecting on a long, finished response, it reflects on each building block before the final answer even takes shape. That’s why the final output stays cleaner, better supported, and much easier to trust.
The easiest way to understand it is to look at how it behaves in a simple question like:
After critiques to evaluate each segment, Self-RAG keeps the ones that actually hold up. The final answer is stitched together from the best-supported pieces, not from everything retrieved.
What you get is a response that reads cleanly, stays close to the evidence, and avoids mixing in unsupported details. Instead of one noisy answer, Self-RAG quietly selects the most reliable fragments and builds a version that makes sense and can be traced back to real supporting text.
Also, Reflection agents can complement Multi-Agent systems by ensuring accuracy and consistency in outputs and we will talk about the Multi-Agent in the next section.
Discover how the Reflection Pattern can improve your workflows with TotalAgility: request a demo now.
More in the Agentic AI Design Patterns series
This article explores one of the core Agentic AI design patterns in depth, while the rest of the series provides detailed breakdowns of the other patterns that shape enterprise-grade AI systems.





